Spectrophotometry is a super helpful tool used in tons of fields to figure out how much light a liquid soaks up. This tells us how much of a substance is in that liquid. To get spot-on and dependable results, you need to know how UV-Vis spectrophotometry works. This guide shares easy tips to make your measurements better. We’ll cover the main ideas, things that mess with your results, and smart ways to use UV-Vis spectrometers.
Principles of Absorbance and UV-Vis Spectrophotometry
Getting the basics of absorbance and UV-Vis spectrophotometry is super important for making sense of your data.
What Is Absorbance in Spectrophotometry?
Absorbance is how much light a sample grabs when light shines through it. It depends on how much stuff is in the liquid and how far the light travels. More light soaked up means a bigger absorbance number.
The Beer-Lambert Law and Its Role in Absorbance Calculations
The Beer-Lambert Law shows how absorbance ties to the amount of stuff and the light’s path. Basically, more stuff or a longer path means more absorbance. Here’s the formula:
A = ϵ ⋅ c ⋅ l
Where:
- A = Absorbance
- ϵ = Molar absorptivity (a special number for each substance)
- c = Amount of the substance
- l = Path length of the sample
This law is a big deal for figuring out how much of something is in a liquid.
Relationship Between Transmittance and Absorbance
Transmittance is the flip side of absorbance. It shows how much light gets through the sample. The two are linked like this:
A = −log(T)
Where:
- A = Absorbance
- T = Transmittance
If less light makes it through, the absorbance number goes up because more light got soaked up.
Factors That Affect Accurate Absorbance Readings
Lots of things can throw off your absorbance numbers. These include how the machine is set up, how you prepare the sample, and what’s going on around you.
Instrumental Factors Influencing Accuracy
Wavelength Accuracy and Bandwidth
The machine has to pick the exact wavelength to get good results. If it’s off or the range is too wide, your data won’t show what the sample is really like. So, setting the wavelength right is a must.
Stray Light and Detector Sensitivity
Stray light is extra light that sneaks into the measurement. It messes things up and gives wrong numbers. The detector’s job is to catch light changes. A top-notch detector with low noise spots tiny differences, making results more accurate.
Sample-Related Variables
Sample Concentration and Path Length
The Beer-Lambert Law says the amount of stuff and the light’s path change absorbance. To keep things steady, make samples with known amounts. Also, use the same path length every time you test.
Solvent Interference and Cuvette Quality
The liquid you mix the sample with shouldn’t soak up much light at your chosen wavelength. If it does, it’ll mess with your results. Plus, the cuvette—the little container for the sample—needs to be clean and scratch-free. Scratches can scatter light and cause mistakes.
Environmental Considerations
Temperature Stability During Measurement
If the temperature keeps changing, it can mess with how the sample acts. This leads to different absorbance numbers. Testing in a steady temperature helps keep your results the same each time.
Cleanliness and Handling of Optical Components
Dirt or smudges on lenses or cuvettes can scatter or soak up light. That ruins your data. Clean the machine’s parts regularly and handle them carefully to keep everything working right.
Best Practices for Using a UV-Vis Spectrometer
To get awesome and trustworthy results, follow these simple steps when using your UV-Vis spectrometer.
Calibration Procedures for Reliable Results
Baseline Correction Techniques
Baseline correction gets rid of extra noise or weird shifts in the machine. First, test a blank sample, usually just the liquid. Then, subtract its absorbance from your sample’s reading. This keeps your data clean and correct.
Use of Reference Standards
Test samples with known absorbance to check the machine. These standards make sure your spectrometer gives steady, accurate numbers every time you use it.
Proper Sample Preparation Techniques
Dilution Methods for High Concentration Samples
If there’s too much stuff in your sample, it can overwhelm the machine. Diluting it brings the absorbance to a good level. Be super careful when diluting so you don’t make errors.
Avoiding Air Bubbles and Contaminants in Cuvettes
Air bubbles or dirt in the cuvette can scatter light. This throws off your results. Fill cuvettes gently and wipe their edges clean before testing.
Measurement Protocols to Reduce Variability
Repeating Measurements for Consistency
To cut down on random mistakes, test the sample a few times. Then, take the average of those numbers. This makes your results more solid and dependable.
Recording Data Under Controlled Conditions
Do your tests in a place where temperature, humidity, and light don’t change much. This keeps your results steady and trustworthy.
Interpreting UV-Vis Spectral Data Effectively
Making sense of the data from your UV-Vis spectrometer is key to making good choices.
Identifying Peak Wavelengths and Maxima (λmax)
The peak wavelength, or λmax, is where the sample soaks up the most light. Finding this spot helps you understand the sample better and makes your measurements sharper.
Quantifying Concentration from Absorbance Values
Using the Beer-Lambert Law, you can calculate how much stuff is in the sample. Just use the absorbance at λmax. This is super common in lab work for figuring out amounts.
Troubleshooting Common Anomalies in Spectra
Sometimes, your data might look weird, like a drifting baseline or odd peaks. These could come from the machine, the sample, or the room. Figuring out what’s wrong helps you fix it and get accurate numbers.
Advanced Features of Modern UV-Vis Spectrometers
Today’s UV-Vis spectrometers have neat features that make them even better and easier to use.
Scanning Speed and Real-Time Data Acquisition
Some machines, like the TU700 UV-Vis spectrometer, scan fast and show data as it happens. This lets you catch changes in absorbance during tests, which is pretty cool.
Multi-Wavelength Analysis Capabilities
Some spectrometers can measure light at lots of wavelengths at the same time. This is great for tricky samples with multiple things that soak up light.
Integration with Software for Data Management
Modern machines hook up with programs to save, study, and show your data. This makes it way easier to keep track of and understand your results.
Brief Introduction to PERSEE as a Trusted Manufacturer
PERSEE is a top-notch company that builds awesome tools, including UV-Vis spectrometers. They’ve been doing this for years and make products for things like environmental tests and drug studies. Their tools are super reliable and work for all kinds of jobs.
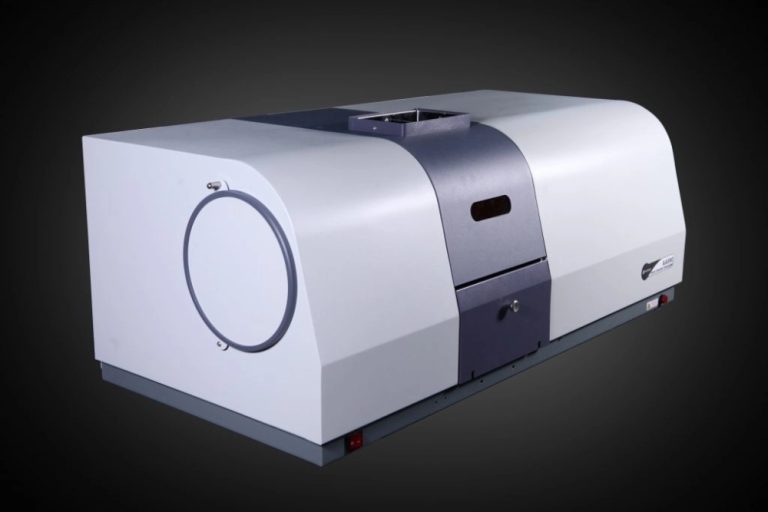
Highlighted Products: TU700 and T8DCS UV/Vis Spectrophotometers
TU700: High-Speed Scanning, Wide Absorbance Range, User-Friendly Interface
The TU700 UV-Vis spectrometer scans quickly and handles a big range of absorbance. Its easy setup makes it great for both simple and tough tasks.

T8DCS: Dual-Beam Design, Enhanced Stability, Versatile Applications
The T8DCS UV-Vis spectrometer has a dual-beam setup for better accuracy and steadiness. It’s perfect for things like environmental checks and quality control.

Industries Served by PERSEE Instruments
PERSEE’s tools are used in lots of areas, like medicine, environmental work, food safety, schools, and farming. People all over the world trust their products for spot-on results. Contact them for more information.
Conclusion
In short, getting great results from spectrophotometry takes some care and smart habits. Know how absorbance works. Watch out for issues with the machine, sample, or room. Use clever testing methods. This way, your UV-Vis results will be accurate and reliable every time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the Beer-Lambert Law, and how is it used in spectrophotometry?
A: The Beer-Lambert Law links absorbance to the amount of stuff and the light’s path. It helps figure out how much of a substance is in a liquid.
Q2: Why is wavelength accuracy important in UV-Vis spectrometry?
A: Picking the right wavelength ensures you measure light correctly. This is key for getting true absorbance numbers.
Q3: How can I reduce stray light in my spectrophotometer?
A: Use high-quality parts. Check the machine often. Prep samples carefully. This keeps stray light low and your data accurate.