- Methodenblick
Nach der Verdauung wird die Probe in einem Graphitofen zerstäubt und die Absorbenz bei 283,3 nm gemessen. Innerhalb eines bestimmten Konzentrationsbereichs ist die Absorptionsfähigkeit von Blei proportional zu seinem Gehalt, und eine quantitative Analyse wird im Vergleich zu einer Standardreihe durchgeführt.
- 2. Instrumente und Reagentien
2.1 Instrumente und Ausrüstung
2.1.1 Erkennungsinstrumente
Graphitofen Atomabsorptionsspektrophotometer (Bleihohlkathodenlampe)
Kühlung Umlaufwassersystem (Nennströmung der Pumpe: 3,5 L/min)
Argongas (Reinheit≥99.99%)
2.1.2 Vorbehandlungsausrüstung
Mikropipetten 1 je 100μL ~ 1000μL, 1000μL ~ 5000μL, 5 ~ 50μL
Volumetrische Flaschen Mehrere 10 mL, 100 mL
Einstellbare elektrische Heißplatte Nenntemperatur: Raumtemperatur ~ 300 ℃
Analytische Gleichgewichtsempfindlichkeit: 1 mg und 0,1 mg
Uhren Brillen Mehrere
Erlenmeyer Flaschen 150ml
2.2 Reagenzien
2.2.1 Reagenzien
Stickstoffsäure (MOS-Klasse)
- 3. Betriebsverfahren
3.1 Probenbehandlung
3.1.1 Vorbereitung der Testlösung
1-2 g der Probe genau (genau 0,001 g) in einen Erlenmeyerkolben abwägen, auf einer elektrischen Heißplatte zur Trockenheit verdampfen, 10 ml Salpetersäure zugeben und auf der Heißplatte verdauen (Referenzbedingungen: 80°C/1 h, 120°C/1 h, 140°C/2 h, 160°C/2 h, Aufheizen auf 180°C). Wenn die Lösung braun ist, fügen Sie mehr Salpetersäure hinzu und verdauen Sie, bis weißer Rauch ausgestrahlt wird. Die Lösung sollte farblos, transparent oder leicht gelb sein. Nach dem Abkühlen verdünnen Sie in einem Volumenkolben mit Wasser auf 10 ml und bereiten Sie gleichzeitig einen Reagenzsrohling vor.
3.1.2 Vorbereitung von Standardlösungen
1) Herstellung von Blei-Standard-Zwischenlösung (1,0 μg/ml):
Pipettieren Sie 0,1 ml der nationalen Blei-Standardlösung genau in einen 100 ml Volumenkolben und verdünnen Sie die Blei-Standardzwischenlösung mit 1,0 μg/ml mit Salpetersäureleisung (99) auf die Marke.
- Vorbereitung der Blei-Standardserie:
Pipettieren Sie 0,0, 0,5, 1,0, 2,0, 3,0 mL der Blei-Standardzwischenlösung (1,0 μg/mL) in 100 mL Volumenkolben und verdünnen Sie mit Salpetersäure (1999) auf die Marke, um Blei-Standardreihen von 0,0, 5,0, 10,0, 20,0, 30,0 ng/mL zu erhalten.
3.2 Probenprüfung
1) Testbedingungen
Referenzbedingungen für das Atomabsorptionsspektrometer im Graphitofen:
Wellenlänge 283,3 nm
Spektrale Bandbreite 0,4 nm
Elementlampe Strom 2,0 mA
Hintergrundkorrekturmethode Deuteriumlampe
Injektionsvolumen 15 μL
- Probentests
Messung der Absorbenz der Standardlösungen, der Rohlösung und der Testlösung in der Reihenfolge. Nehmen Sie die Absorbenz der Null-Standardlösung von der jeder Standardlösung ab, zeichnen Sie eine Arbeitskurve mit Massenkonzentration als Abszisse und entsprechender Absorbenz als Ordinate auf. Bestimmen Sie die Massenkonzentration von Blei in der Testlösung aus der Arbeitskurve anhand seiner gemessenen Absorbenz.
3.3 Ergebnisberechnung
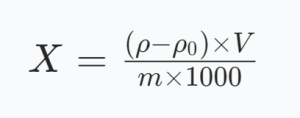
Wo:
X: Bleigehalt in der Probe, in Milligramm pro Kilogramm (mg/kg);
ρ: Massenkonzentration von Blei in der Probenlösung, in Nanogramm pro Milliliter (ng/ml);
ρ0: Massenkonzentration von Blei in der Rohlösung, in Nanogramm pro Milliliter (ng/ml);
V: Volumen der Probenveradungslösung nach konstantem Volumen, in Millilitern (mL);
m: Probengewicht in Gramm (g);
1000: Umwandlungskoeffizient.

