Газовая спектрометрия является основой современной аналитической науки. Он обеспечивает точный, быстрый и целенаправленный анализ газообразных соединений во многих областях. Подход использует то, как световые или энергичные частицы связываются с молекулами газа. Эта связь дает четкие и измеримые детали.
Роль спектрометрии в анализе газов
Главная задача газовой спектрометрии заключается в обнаружении и измерении газообразных соединений с большой точностью. Он делает это, проверяя, как молекулы газовой фазы реагируют на электромагнитное излучение или ионизирующую энергию. Они действуют как молекулярные отпечатки пальцев. Аналитики могут использовать их для идентификации конкретных соединений, даже в сложных смесях.
Спектральные данные из этих инструментов помогают найти как тип, так и количество газов. Такие навыки имеют жизненно важное значение для наблюдения за окружающей средой, управления промышленными процессами и соблюдения правил.
Основные механизмы газовых спектрометров
Прежде чем посмотреть на методы, это помогает понять основные способы обнаружения, которые поддерживают газовые спектрометры: Абсорбция: Молекулы принимают определенные длины волн излучения. Это меняет силу проходящего света. Эмиссия: возбужденные молекулы выделяют энергию, когда они падают до более низкого уровня энергии. Рассеяние: входящее излучение отскачивает от молекул в разных направлениях и сильностях.
Различные спектроскопические методы используют эти способы с определенными частями электромагнитного спектра или заряженными частицами. Например, инфракрасный (ИК) сигнал направлен на молекулярные вибрации. UV-Visible (UV-Vis) занимается электронными сменами. Массовая спектрометрия (МС) сортирует ионы по соотношению массы к заряду. Шаги обработки сигнала и калибровки повышают точность. Они устраняют проблемы с изменениями инструмента и внешними эффектами.
Виды спектроскопических методов, используемых в анализе газов
Выбор спектроскопической техники зависит от целевого вещества’ с молекулярными чертами. Каждый метод приносит четкие преимущества, основанные на чувствительности, выборе и рабочих условиях.
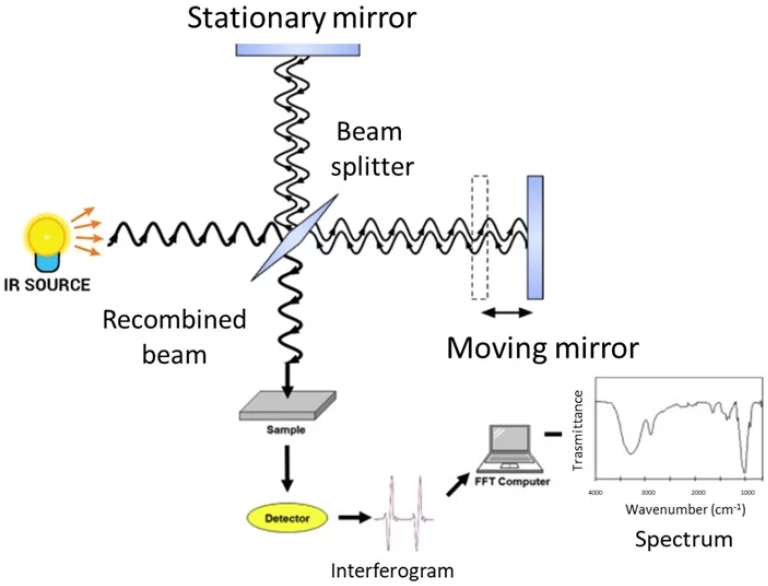
Инфракрасная (ИК) спектроскопия для обнаружения газов
ИК-спектроскопия работает на идее, что молекулы поглощают ИК-излучение с типичными вибрационными скоростями. Это делает его очень хорошим для поиска органических паров и парниковых газов, таких как CO ₂, CH₄, и нет ₓ.
Инфракрасные спектрометры с трансформацией Фурье (FTIR) широко используются. Они обеспечивают: лучшее разрешение, быстрее сканирование, улучшенную чувствительность
FTIR8000 и FTIR8100 от Перси предлагает надежную работу с высоким разрешением для многих задач анализа газов.
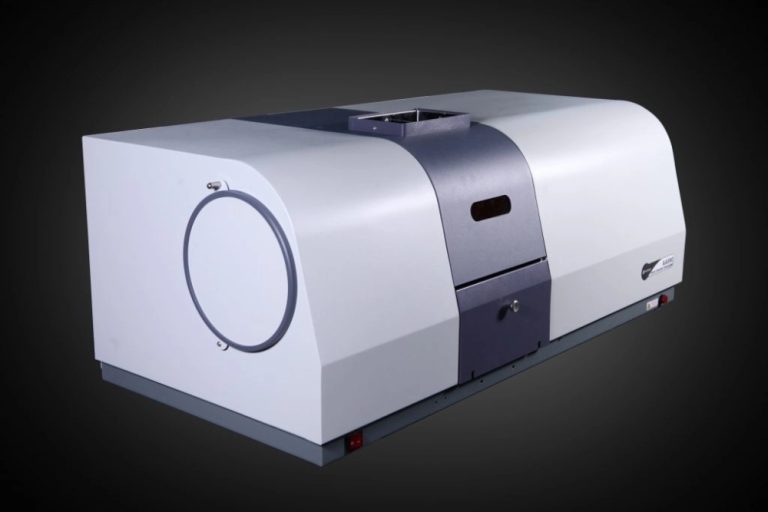
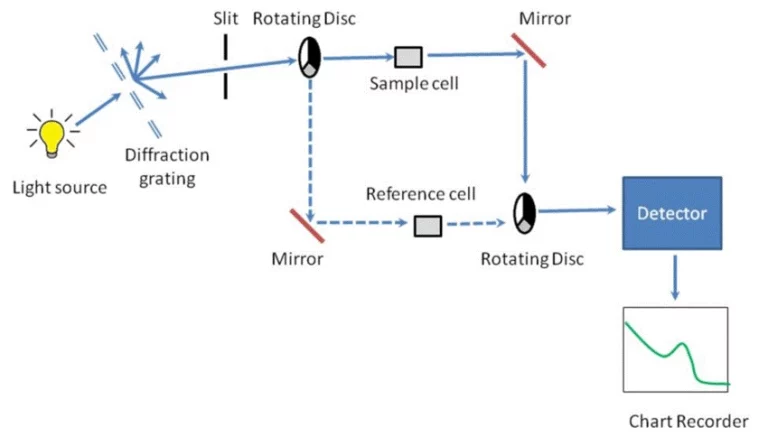
Ультрафиолетовая видимая (UV-Vis) спектроскопия в газообразной среде
Спектроскопия UV-Vis подходит для газов, которые показывают электронные сдвиги в ультрафиолетовом и видимом диапазоне. Примерами являются озон (O) ₃), диоксид азота (НЕ) ₂), и диоксид серы (SO) ₂). Для правильного обнаружения газовой фазы настройка длины волны должна быть точной. Это позволяет избежать спектрального перекрытия. Спектрофотометр TU700 UV/Vis от PERSEE имеет скорость сканирования 30 000 нм/мин. Он завершает спектроскопическое сканирование всего за 2 секунды. Таким образом, он подходит для настроек высокого объема. Кроме того, спектрофотометр UV-Vis T8DCS использует монохроматор Черни-Тернер с голографической решеткой. Эта настройка отрезает блуждающий свет и дает хорошую оптическую ясность.
Массоспектрометрия (МС) для анализа состава газа
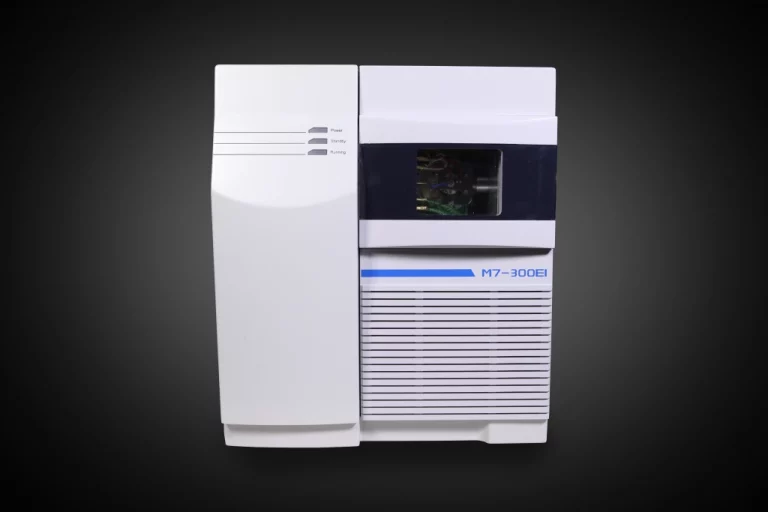
Массоспектрометрия сияет своей максимальной чувствительностью и способностью проверять детали на уровне следов. Образец ионизируется и распадается, часто с помощью ионного источника воздействия электронов. Больше ударов делают ионы расщепляться. Затем ионы попадают в массовый анализатор. Там они сортируются по значению m/z или соотношению массы к заряду. В газовой хроматографии-массовой спектрометрии (GC-MS) МС улучшает обнаружение соединений после разделения хроматографией. Система PERSEE M7 Single Quadrupole GC-MS позволяет такое соединение для правильного профилирования газового состава.
Компоненты приборов газового спектрометра

Успех любого газового спектрометра зависит не только от его метода обнаружения, но и от того, как построены его основные части.
Оптические системы и детекторы
Настройка оптического пути напрямую влияет на мощность и остроту сигнала. Детекторы очень важны. Они превращают входящие фотоны или ионы в электрические сигналы, которые мы можем измерить. Это зависит от спектральной области: фотодиоды работают для UV-Vis-обнаружения. Болометры или термопары обрабатывают IR. фотомножительные трубки (PMT) выбираются для их сильной реакции в темном свете. В T8DCS Использует фотомножительную трубку в качестве детектора. Он дает выдающуюся чувствительность.
Модули введения образцов и кондиционирования
Сохранение качества образца является ключевым. Газы из воздуха или процессных потоков часто нуждаются в подготовке перед анализом. Он включает в себя фильтры, очищающие частицы, контроль давления стабилизирует поток, температурные единицы останавливают накопление влаги или разрыв. Эти настройки делают результаты повторимыми. Они также блокируют ошибки от грязи или смешаний.
Системы калибровки и эталонные стандарты
Правильное измерение зависит от хорошей калибровки. Это означает использование утвержденных калибровочных газов для установки уровней реакции, эталонных ячеек для исправлений отправной точки, автоматических процессов для систем постоянного наблюдения за выбросами (CEMS).
Параметры производительности, влияющие на аналитическое качество
Помимо выбора технологии, некоторые факторы определяют надежность газоспектрометрических показаний.
Ограничения чувствительности и обнаружения в газовой спектрометрии
Чувствительность обусловлена производительностью детектора, размером оптического пути, уменьшением фонового шума, более низкими пределами пятен для проверки окружающей среды или поиска вредных газов. Инструменты, такие как GC/MS, могут поднимать уровни до частей на триллион.
Селективность по отношению к целевым газам среди сложных матриц
Селективность обеспечивает правильное чтение даже в смесях. Способы этого включают в себя жесткие спектральные фильтры, высокодетальные анализаторы массы, исправления для перекрытия через математические шаги, детекторы селективной массы обнаруживают части из массового спектра. В сочетании с ГК он становится самым мощным инструментом идентификации.
Время реагирования и стабильность в эксплуатационных условиях
Быстрое время реакции имеет важное значение при изменении систем, таких как заводские реакторы. Стабильность сохраняет работу даже при сменах тепла или давления. TU700 имеет диапазон поглощения от -4 до 4 Abs. Он управляет образцами высокой концентрации в различных условиях.
Интеграция с аналитическими рабочими процессами и системами автоматизации
Газовые спектрометры должны хорошо вписываться в более крупные процессы, чтобы быть полезными в реальной жизни.
Соединение с хроматографическими методами (GC-MS, GC-FID)
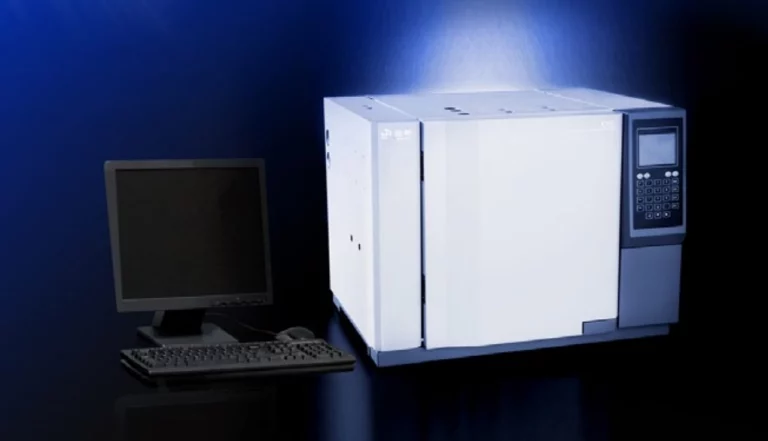
Хроматография делит соединения перед спектрометрическими проверками. Газовая хроматография (ГХ) делит части смеси. Затем каждую часть можно назвать и измерить.
GC G5 PERSEE работает с дополнительными детекторами, такими как FID/TCD/ECD. Он дает варианты для таких задач, как проверка ЛОС или заводская проверка качества.
Роль в системах непрерывного мониторинга выбросов (CEMS) и анализе процессов (PAT)
Спектрометры, встроенные в CEMS, дают данные в режиме реального времени для соблюдения правил. В настройках PAT круги обратной связи сразу же корректируют настройки процесса. Инструменты PERSEE связаны с системами SCADA. Они отправляют автоматические предупреждения и данные журнала. Это стимулирует рабочий поток.
PERSEE: надежный производитель передовых аналитических приборов
PERSEE стала ведущим мировым игроком в области аналитических инструментов. Он имеет полный ассортимент продукции, созданной для нужд науки и промышленности.
Обзор технологических возможностей PERSEE
PERSEE - новая высокотехнологичная компания, основанная в 1991 году. Более 30% его сотрудников сосредоточены на исследованиях и разработках. PERSEE подчеркивает новые идеи и тщательную науку в своих продуктовых группах. Продукты включают FTIR, GC, AAS, UV-VIS, рентгеновские инструменты и другие.
M7 FTIR газовый анализатор
Он построен для проверки многих типов газов с высокодетальной технологией FTIR. Он подходит для наблюдения за окружающей средой и заводских испытаний выбросов.
Газовый хроматограф G5GC
Он поставляется с дополнительными детекторами, такими как FID / TCD / ECD. Он хорошо работает для ЛОС в проверке качества воздуха или заводском контроле.
Ключевые концепции, охватывающие основы газовой спектрометрии
Газовая спектрометрия использует основные связи между молекулами газа и типами энергии, такими как свет или ионы. Каждый метод - IR, UV-Vis, MS - приносит особые сильные стороны. Они зависят от целевых веществ, сложности смешивания и целей использования. Его роль охватывает области от экологической работы до производства наркотиков. Это связано с его точностью, скоростью, гибкостью и простой адаптацией к текущим процессам.
PERSEE является ведущим производителем, сосредоточенным на исследованиях, производстве и продаже передовых аналитических инструментов с 1991 года. С одобрениями, такими как ISO9001, ISO14001, OHSAS18001 и маркировка CE, PERSEE держит строгие проверки качества. Его широкий набор продуктов включает в себя спектрофотометры UV-VIS, такие как ТУ700 и серии T8DCS, системы FTIR, газовые хроматографы, как Г5ГКи комбинированных решений. Они подходят для образования, окружающей среды, фармацевтики, сельского хозяйства, нефтехимии и многого другого.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Q1: Какие факторы следует учитывать при выборе газового спектрометра?
А1: Выбор зависит от типа вещества, необходимых пределов пятнения, сложности смешивания, потребностей в стабильности тепла/давления, стандартов правил и соответствия текущим аналитическим настройкам.
Q2: Чем FTIR отличается от УФ-спектроскопии в газовом анализе?
A2: FTIR проверяет молекулярные вибрации с помощью среднего инфракрасного света. Подходит для органических газов. УФ-спектроскопия изучает электронные сдвиги в неорганических газах, таких как озон или диоксид азота.
Q3: Могут ли газовые спектрометры использоваться для мониторинга в реальном времени?
А3: Да. Современные инструменты от PERSEE позволяют постоянно проводить измерения с быстрым временем реакции. Они подходят для использования в реальном времени, таких как процессы CEMS или PAT.