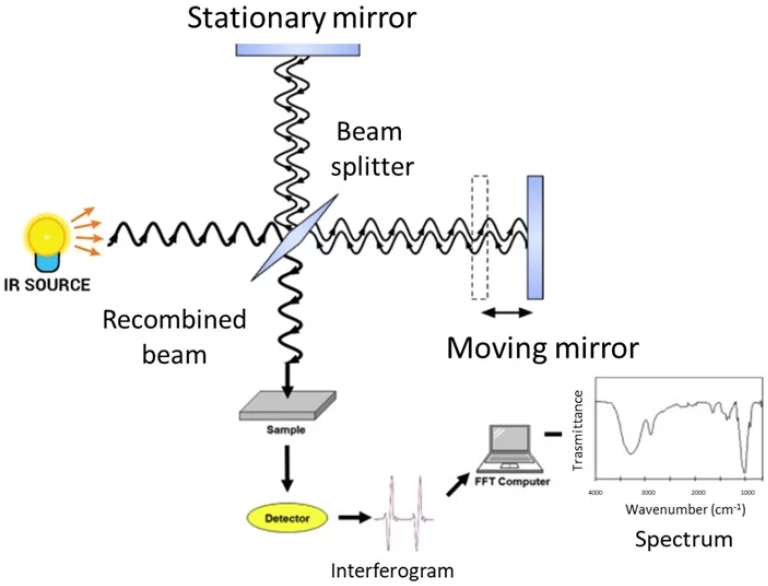
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) serves as a combined analytical method that merges the separation strengths of gas chromatography (GC) with the strong identification abilities of mass spectrometry (MS). In GC, volatile substances get separated mainly through variations in their boiling points and how they interact with the fixed phase inside the column. This process lets compounds from tricky mixtures come out at distinct times. As a result, it becomes easier to handle complex samples.
After separation, these substances enter a mass spectrometer. There, they become ionized and break apart into smaller pieces. The process starts when the sample faces a stream of high-energy electrons, and these electrons knock off an electron from the molecule, creating a positive ion through simple repulsive forces. More impacts then cause these ions to split further. Next, the machine sorts these fragments based on their mass-to-charge (m/z) values, and it uses devices like quadrupoles or time-of-flight (TOF) setups for this task.
What Configurations Make GC-MS Instruments Effective?
A standard GC-MS setup includes key parts such as a spot for injecting the sample, a thin capillary GC column, an area to create ions, a device to sort masses, and a sensor to pick up signals. Among mass sorters, the quadrupole ion-trap type stands out in GC-MS, and it keeps gas-based negative or positive particles trapped for extended times using electric and magnetic forces.
Today’s setups often use precise TOF sorters. These give spot-on mass readings, which help tell apart items with close basic masses. While basic QMS and TQMS handle rough mass values, TOFMS offers sharp detail, reaching accuracy around 1/1000. Strong vacuum setups and smart software for gathering data also play vital roles, and they keep the whole system steady and produce clear, useful outcomes.
How Should Samples Be Prepared for Complex Matrix Analysis?
Good prep work boosts how well the method detects things and cuts down on unwanted mix-ups. Common ways include solid-phase microextraction (SPME), stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE), and QuEChERS for handling volatile and somewhat volatile items. Such methods pull together the targets while lowering issues from the surrounding stuff that might hide important signals.
Choices depend on factors like how sticky the target is to water, how messy the background gets, and how much of the item exists. For example, QuEChERS works great for checking pesticide leftovers in food, and its straightforward steps and wide reach for different targets make it a top pick.
Why Is Derivatization Sometimes Necessary?
When dealing with sticky or heat-sensitive items, changing their form through derivatization often proves essential, and this step raises their ability to turn into gas or become easier to spot. Methods such as silylation, acylation, and alkylation tweak active parts to form versions with better flow in the column and useful break patterns. These changes can shift how we read the mass signals a lot. They create special fragments that help pinpoint what the substance really is.
What Advanced GC-MS Techniques Enhance Analytical Power?
GC×GC-MS adds a second column set at a right angle to the first one, connected through a quick switch system. This arrangement boosts how many peaks fit without overlap and sharpens the split of items that come out together, and it shines in fields like oil processing and checking the environment, especially where samples are packed in a lot of different parts.
What Benefits Does Tandem MS Provide?
Tandem MS (MS/MS) carries out back-to-back mass sorting with a break step in the middle for splitting. This tool, which handles two rounds of mass separation through tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS), brings strong selectivity. As such, it fits well for measuring amounts in samples full of complications and distractions. Using collision-induced dissociation (CID), it makes smaller ions from chosen starting ones. This helps figure out structures and measure targets accurately, even when other things get in the way.
How Does High-Resolution MS Enable Non-Targeted Screening?
High-resolution MS delivers exact mass info, which matters a great deal for spotting unknown items without just checking against stored patterns. A sharp mass-resolution TOFMS can pick out strange compounds on its own, without needing library matches, and it suits broad searches for anything present. Such features matter hugely in environmental checks and studies of body chemicals, where new findings often appear.
How Can GC-MS Data Be Processed Effectively?
Programs hold a central spot in sorting out blended peaks and linking patterns to stored collections. Still, troubles pop up with look-alike isomers that break in nearly the same ways. So, auto systems need fine-tuning to deliver trustworthy matches.
How Is Chemometrics Applied in GC-MS Data Interpretation?
Tools from chemometrics, including principal component analysis (PCA), partial least squares (PLS), and grouping by levels, pull out trends from big piles of info. They support sorting items into groups and spotting shifts in fields like verifying food origins, body chemical mapping, and poison checks in forensics.
Where Is GC-MS Most Impactful?
GC-MS forms a key pillar for finding lasting organic pollutants (POPs), pesticides, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and somewhat volatile organics in air, water, and soil. Its sharp focus allows tiny amount measurements, which regulators rely on for rules.
What Role Does It Play in Metabolomics?
In health studies, GC-MS maps natural body chemicals from fluids or body parts. It uses aimed and open-ended paths. This aids in finding signs of issues and tracing disease paths via fast, large-scale runs.
How Does It Contribute to Food Safety?
Proven GC-MS steps guard food quality by spotting unwanted items like pesticide traces, banned extras, fake additions, and scent makers. Its keen eye spots them even in thick food setups.
What About Petrochemical Applications?
During oil refining, GC×GC-MS maps out carbon chains and adds elements like sulfur or nitrogen types. This fine detail backs checks on quality and tweaks to processes in oil-related tasks.
Which Instruments Best Suit Specific Analytical Needs?
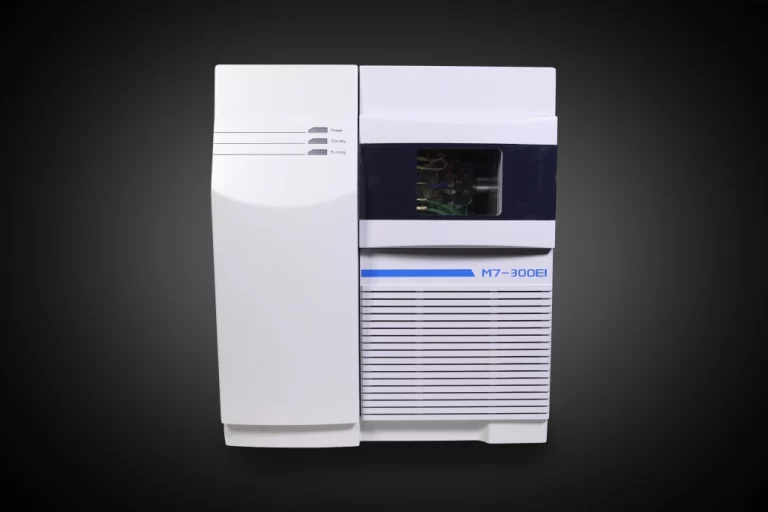
The M7 Single Quadrupole GC-MS from Persee stands as a fresh, top-performing setup built for everyday checks and deeper studies. It has a unique dual-filament EI source that ionizes well, a tough vacuum with a turbo molecular pump, a pull-out quadrupole pre-filter to cut dirt risks, and easy-to-use software for control from afar. It suits tasks from food checks to guarding the environment, and you can learn more about the M7 Single Quadrupole GC-MS here. Feel free to contact PERSEE!
Why Consider the G5 GC for Routine Analysis?
The G5 GC brings flexible modules, allowing up to three detectors at once, such as FID, TCD, ECD, and more. It comes with smart software that watches in real time and handles various ways to add samples. With a big oven for multi-column work and quick cool-downs, it fits busy settings. Check out details on the G5 GC system here.
How Can Analytical Integrity Be Maintained Over Time?
Regular checks keep output steady. Tuning with perfluorotributylamine (PFTBA) or similar benchmarks holds mass precision and even sensor replies as time passes.
How to Minimize Contamination Risks?
Steady upkeep involves swapping inlet liners, septa, and prepping columns often. Plans for column prep, septa care, and liner changes stop leftover traces or fake peaks that harm the result’s trust.
Insights on the Role of GC-MS in Complex Mixture Analysis
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry keeps its place as a main tool because of its rare skill in breaking down tough blends with great detail.
FAQ (Pertanyaan umum)
Q1: What is the benefit of using two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC×GC) over traditional 1D-GC?
A1: GC×GC provides enhanced separation capacity by combining two orthogonal columns. This allows better resolution of complex samples with many co-eluting compounds that traditional 1D-GC may not adequately separate.
Q2: How does tandem mass spectrometry improve compound identification?
A2: Tandem MS enables fragmentation of selected precursor ions to generate product ion spectra. This additional layer of structural information enhances specificity in identifying compounds within complex matrices.
Q3: Why is derivatization important before GC-MS analysis?
A3: Derivatization improves the volatility or thermal stability of certain analytes that are otherwise not amenable to gas-phase analysis. It also enhances detectability by producing more favorable fragmentation patterns.