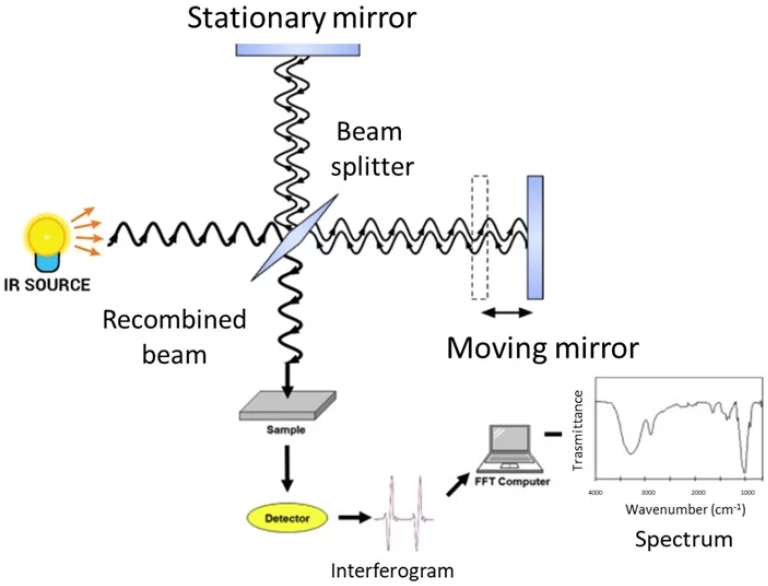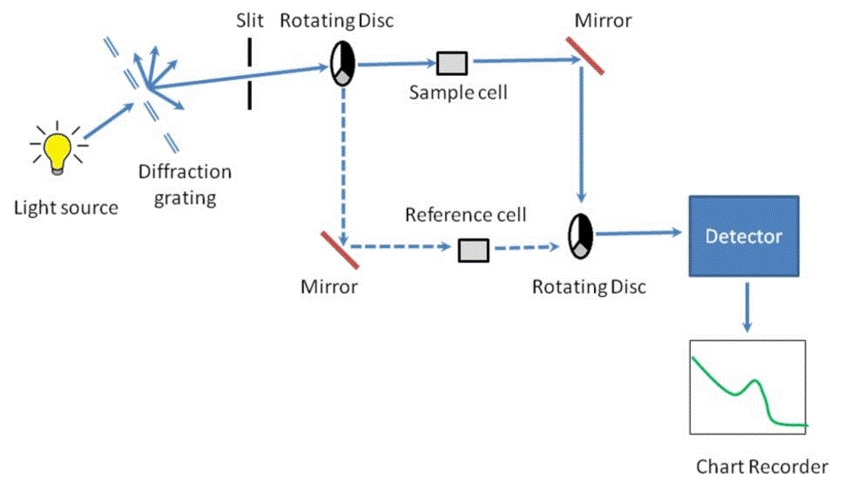
En spectroscopie à double faisceau, la lumière entrant d'une seule source se divise en deux voies différentes. Un chemin envoie la lumière à travers l'échantillon. L'autre chemin le dirige à travers une référence. Cette façon de diviser la lumière optiquement est généralement manipulée par un découpeur de faisceau. Parfois, un miroir semi-transparent fait le travail à la place. Le faisceau d'énergie ou de lumière commence à partir de la source. Cette source pourrait être une lampe à cathode creuse ou une lampe à décharge de vapeur. Un hélicoptère rotatif le divise ensuite en une poutre de référence et une poutre d'échantillon. Après cela, ces poutres reviennent ensemble. Ils se déplacent à travers un monochromateur. Ce dispositif sélectionne certaines longueurs d'onde. Ce sont ceux qui nous intéressent pour mesurer.
Cette configuration apporte un véritable coup de pouce par rapport aux systèmes à faisceau unique. Les spectrophotomètres à faisceau unique nécessitent un blanchiment manuel. Ou ils nécessitent des étapes faites l'une après l'autre. Les systèmes à double faisceau vous permettent de regarder les signaux de référence et d'échantillonnage en même temps. La comparaison se fait tout de suite. Il réduit la dérive de base. Cette dérive provient des changements dans l'intensité de la source lumineuse. Il provient également des changements de sensibilité du détecteur. Cela permet une meilleure stabilité dans l’analyse.
Quels sont les composants clés d'un spectrophotomètre à double faisceau?
Le système a souvent une source lumineuse avec une bonne stabilité. Cela donne une lumière constante à travers les rayons UV et visibles. Il utilise des grilles holographiques. Ceux-ci aident à maintenir la lumière errante basse. Ils identifient également les longueurs d'onde exactes. Le monochromateur à grille extrait la longueur d'onde analytique du métal en question. Il sépare cela de toute autre énergie lumineuse dans le faisceau.
Les détecteurs tels que les tubes photomultiplicateurs ou les photodiodes de silicium changent les signaux optiques en signaux électriques. Ensuite, les amplificateurs de signal et les ADC les traitent. Les systèmes plus récents ajoutent une automatisation gérée par logiciel. Cela maintient la précision de la longueur d'onde au point. Il maintient également la linéarité photométrique constante pendant les mesures.
Quel est le flux de travail analytique standard en spectroscopie à double faisceau?
Une bonne préparation des échantillons commence par la cueillette de solvants qui fonctionnent bien ensemble. Vous devez également vous assurer que les cuvettes sont propres. Ils doivent également correspondre optiquement. Si des erreurs se produisent ici, elles peuvent se propager à travers toute l'analyse. Le faisceau de référence aide à la correction de base. Il compense l'absorption de fond par les solvants ou cuvettes. De cette façon, vous obtenez une vraie lecture de l'absorbance de l'analyte.
Les systèmes à double faisceau s'en occupent seuls. Ils continuent de comparer l'absorbance de l'échantillon au chemin vide ou de référence. La comparaison ne s’arrête jamais. Cette approche à deux faisceaux annule les problèmes tels que le clignotement de la lampe. Il traite également du bruit optique. Ainsi, le processus reste lisse et fiable.
Comment les mesures sont-elles acquises à haute fidélité du signal ?
Lors de la collecte de données, l'instrument commute entre le faisceau de référence et le faisceau d'échantillon. Il le fait à tour de tour. Un chopper rotatif ou un interrupteur électronique maintient tout en synchronisation. Pour rendre le signal plus fort et plus clair, ils utilisent la moyenne du signal numérique. Cela réduit le bruit aléatoire. Cela augmente la répétitivité des résultats. Les gens moyennent souvent les signaux pour compenser les points difficiles. Mais le bruit de lumière errante est différent. C'est toujours positif. D'autres bruits aléatoires vont dans les deux sens.
Comment l'absorption et la concentration sont-elles calculées en spectroscopie à double faisceau?
Vous trouvez l'absorbance, appelée A, à partir de la transmittance, qui est T. La formule est A = -log(T). Et T égal I sur I ₀. Je suis l'intensité de la lumière à travers l'échantillon. I₀ est l'intensité à travers le chemin de référence. Obtenir I ₀ Le droit compte beaucoup. Si elle dérive, les nombres d'absorbance changent aussi. La loi dit que A = εlc. Ici, ε est l'absorptivité molaire. Et l est la longueur du chemin. Pour réaliser des courbes d'étalonnage, tracez l'absorbance par rapport aux concentrations connues. Cela vous permet d'estimer les inconnus en lisant entre les lignes. La lumière qu'un échantillon absorbe à une longueur d'onde donnée se lie directement à sa concentration.
Quelles techniques de correction sont utilisées pour la dérive instrumentale?
Vous pouvez combattre la dérive instrumentale avec des photodétecteurs doubles. Ils corrigent en temps réel. Cela maintient les mesures de référence stables tout au long du chemin. Les instruments modernes utilisent également des logiciels pour la stabilisation de base. Il corrige la dérive à long terme. Il gère également le bruit de fond.
Quels facteurs peuvent compromettre la précision des mesures à double faisceau?

L'étalonnage régulier avec des matériaux certifiés fixe l'alignement. Il vérifie également la précision de la longueur d'onde. Vous testez la linéarité, la longueur d'onde, la bande passante et la lumière errante avec des normes chimiques de suite.
Comment les effets de matrice d'échantillon faussent-ils les résultats?
Matrices dures apportent dispersion, fluorescence ou turbidité. Ces bouleversements avec une réelle absorbance. Vous pouvez réduire les torsions spectrales avec la soustraction de fond. Ou choisissez des plages de longueur d'onde qui ne sont pas fortement touchées par les problèmes de matrice.
Quelles applications avancées bénéficient de l'architecture à double faisceau ?
Le balayage continu et les corrections instantanées du signal rendent les systèmes à double faisceau excellents pour suivre la cinétique de la réaction. Pensez aux analyses enzymatiques ou au travail de photodégradation. Le Spectrophotomètre UV-Vis T7D a des fonctions cinétiques intégrées dans son logiciel. Le T7D/T7DS est capable d'effectuer des mesures photométriques, des balayages de spectre, des déterminations quantitatives et de l'analyse ADN/protéine.
Comment l'analyse multi-longueur d'onde est-elle effectuée pour les mélanges complexes?
La déconvolution spectrale permet de mesurer de nombreux analytes à la fois. Vous regardez l'absorbance sur plusieurs longueurs d'onde. Cela aide beaucoup avec des mélanges délicats dans des échantillons pharmaceutiques ou environnementaux.
Pourquoi PERSEE fait-il confiance aux solutions de spectroscopie analytique ?
PERSEE a gagné son nom grâce à des idées nouvelles et à une ingénierie précise. Sa gamme de spectrophotomètres UV-Vis comprend des modèles de pointe comme le Spectrophotomètre UV-Vis T8DCSCeux-ci offrent des bandes passantes variables de 0,1 à 5 nm. Ils ont une détection photomultiplicateur pour une forte sensibilité. Les grilles holographiques coupent la lumière errante. T8DCS est un spectrophotomètre à faisceau double haute performance avec une bande passante spectrale sélectionnable en continu de 0,1 à 5nm. En outre, les produits de PERSEE couvrent la chromatographie à gaz et la spectrométrie de masse. Exemples sont les systèmes M7 Single Quadrupole GC-MS et G5 GC. Ils répondent aux besoins des contrôles environnementaux au contrôle de la qualité pharmaceutique.
Qu’est-ce qui distingue l’infrastructure de soutien de PERSEE à l’échelle mondiale ?
Persan Il est basé à Pékin. Il gère des opérations dans le monde entier. Il sert des dizaines de milliers de professionnels. Beijing Purkinje General Instrument Co., Ltd. est un entreprise moderne de haute technologie qui a été fondée en 1991. La société a des certifications comme ISO9001, ISO14001, OHSAS18001 et CE. Le support comprend le diagnostic à distance, des logiciels personnalisés et des équipes locales.
Que devraient les experts garder à l'esprit lors de l'utilisation de systèmes à double faisceau?
Faire des contrôles d'étalonnage souvent. Remplacez les lampes au besoin. Vérifiez régulièrement l’alignement. Les experts devraient également vérifier les paramètres du logiciel. Regardez les bandes passantes spectrales, les gains de détecteur et les algorithmes de correction. Alignez-les à votre tâche. Choisissez en fonction de ce que vous devez analyser. Pour une cinétique fine, optez pour des scanners rapides avec détection de PMT. Pharma QA peut nécessiter une faible lumière errante et des bandes passantes réglables. Les laboratoires environnementaux veulent des constructions robustes et une large couverture de longueur d'onde.
FAQ (questions fréquentes)
Q1: Quel est le principal avantage de la spectroscopie à faisceau double par rapport à la spectroscopie à faisceau unique?
A1: La spectroscopie à double faisceau permet de mesurer simultanément l'échantillon et les faisceaux de référence, réduisant ainsi les erreurs dues aux fluctuations de la source lumineuse ou à la dérive du détecteur.
Q2: Comment l'absorbance est-elle calculée dans un spectrophotomètre à double faisceau?
A2: L'absorption est calculée en utilisant la formule A = -log(I/I) ₀), où je suis l'intensité à travers le chemin de l'échantillon et je ₀ est par le chemin de référence.
Q3: Les spectrophotomètres à double faisceau peuvent-ils être utilisés pour l'analyse quantitative?
A3: Oui, ils sont idéaux pour l'analyse quantitative lorsqu'ils sont combinés avec des courbes d'étalonnage basées sur la loi de Beer-Lambert en utilisant des concentrations standard connues.